搜索
Title: Light-Directed Liquid Manipulation in Flexible Bilayer Microtubes
Author: Bo Xu, Chongyu Zhu, Lang Qin, Jia Wei, Yanlei Yu*
Journal: Small, 2019, 15(24), 1901847. (Cover Paper)
Abstract:
Flexible microfluidic systems have potential in wearable and implantable medical applications. Directional liquid transportation in these systems typically requires mechanical pumps, gas tanks,and magnetic actuators. Herein, an alternative strategy is presented for light-directed liquid manipulation in flexible bilayer microtubes, which are composed of a commercially available supporting layer and the photodeformable layer of a newly designed azobenzene-containing linear liquid crystal copolymer. Upon moderate visible light irradiation, various liquid slugs confined in the flexible microtubes are driven in the preset direction over along distance due to photodeformation-induced asymmetric capillary forces.Several light-driven prototypes of parallel array, closed-loop channel, and multiple micropump are established by the flexible bilayer microtubes to achieve liquid manipulation. Furthermore,an example of a wearable device attached to a finger for light-directed liquid motion is demonstrated in different gestures. These unique photo controllable flexible microtubes offer a novel concept of wearable microfluidics.
This paper was selected as cover paper for Small 24/2019.

论文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/smll.201901847
PDF下载:![]() Light-Directed Liquid Manipulation in Flexible Bilayer Microtubes.pdf
Light-Directed Liquid Manipulation in Flexible Bilayer Microtubes.pdf
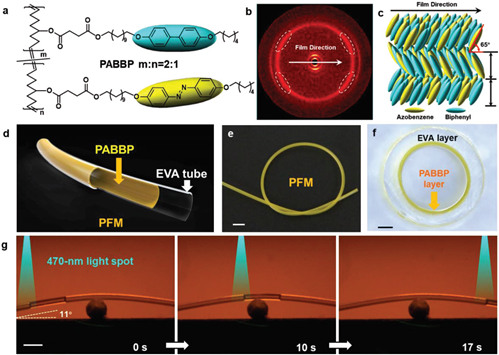
利用联苯和偶氮苯基元的协同效应,本工作设计并合成了一种具有良好力学性能的光响应线型液晶高分子PABBP,其弹性模量可与商用EVA软管匹配,进而与EVA软管复合构筑出双层微管执行器。此外,联苯基元的引入能够增加PABBP层中的光照穿透深度,提高光致形变能力,带动超过自身四倍厚度的非响应层EVA管产生形变。同时,PABBP层具有一定的自修复性能,受损断裂后,在紫外光照射下发生光致流体化,可与EVA层重新贴合,恢复液体运输功能,有效提升双层微管执行器的稳定性以及使用寿命。