搜索
Title: Phototunable Morpho Butterfly Microstructures Modified by Liquid Crystal Polymers
Author: Xin Qing, Yuyun Liu, Jia Wei, Ran Zheng, Chongyu Zhu, Yanlei Yu*
Journal: Adv. Optical Mater., 2019, 7(3), 1801494.
Abstract:
The unique hierarchical microstructures of the Morpho butterfly wing (MBW) exhibit angle independent blue iridescence. Biomimicking these microstructures and turning them into functional photonic crystals (PhCs) have fascinated scientists yet remain challenging. Here, a phototunable PhC is fabricated by depositing the azobenzene‐containing linear liquid crystal polymer (LLCP) onto the MBW template. Thanks to the excellent mechanical properties and deformability of LLCP, the generated 3D bilayer microstructures demonstrate hierarchical deformation upon UV light irradiation, leading to a blueshift of the reflection peak (70 nm) and a remarkable change of reflectance (40%). This phototunable PhC may have potential applications in pigments, cosmetics, and sensors.
论文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adom.201801494
PDF下载:![]() Phototunable Morpho Butterfly Microstructures Modified by Liquid Crystal Polymers.pdf
Phototunable Morpho Butterfly Microstructures Modified by Liquid Crystal Polymers.pdf
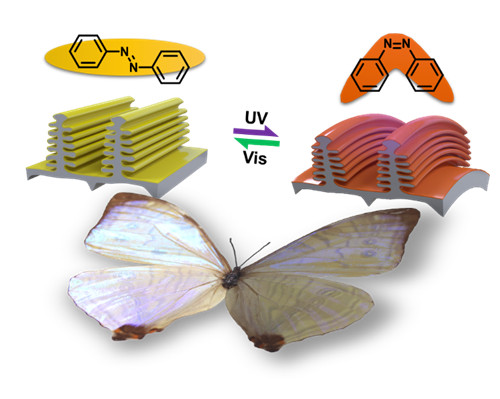
本文展示了一种通过将含偶氮苯的线性液晶聚合物涂覆到闪蝶翼(MBW)上来制造具有分级微结构的光可调光子晶体(PhC)的新方法。LLCP通过静电纺丝沉积在MBW表面上,将LLCP溶液转化为干燥的微尺度纤维,而不会改变微观结构。进一步的熔化和退火工艺在MBW上产生了取向良好的LLCP涂层,以实现光响应LLCP-MBW复合材料。MBW的分级微观结构在低能紫外光照射下会发生明显变形,包括鳞片、脊,甚至片层间距。通过对结构-反射关系的详细分析,证明了LLCP-MBW分级微结构的变形可以通过光强度来调控,从而导致反射峰的大蓝移,实现了反射强度的可控调节。此外,反射率的变化可以通过可见光恢复,有望能应用于光传感领域。